Effects of a Stroke on the Brain and Body
When blood supply is cut off from the brain, cells start to die from lack of oxygen. Within minutes, skills, such as reasoning, speech, and some degree of arm, leg, or facial movement, may be lost. The type of skills and the amount of loss depend on which part of the brain was affected, and how much tissue was damaged.
-
The brain is the body’s control center, which handles communication, motor, sensory, and processing functions.
-
The cerebellum controls the body’s coordination and balance.
-
The brain stem links the brain and the spinal cord. It also handles basic body functions.
-
The spinal cord carries messages between the brain and the body.
A stroke causes lost skills
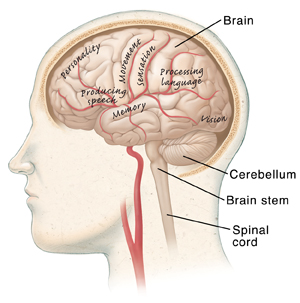
Each part of the brain has a role related to a function in the body. Damage to any part of the brain limits its ability to carry out its role. This results in lost skills or changes in function, and even in personality. Some parts of the brain and its related functions that may be affected by stroke are as follows:
-
The front of the brain houses reasoning and the ability to control emotions. Personality lives here.
-
The left side of the brain controls the right side of the body. It also handles speech, language, reading, and writing.
-
The right side of the brain controls the left side of the body.
-
The back of the brain controls vision.
-
The brain stem handles breathing and swallowing.
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.